Multiple Tier-1 Gateway VPNs – Understanding Networking and Security Configurations
Tier-1 gateways can terminate VPNs for multi-tenancy environments, where direct connectivity over the VPN is required by a tenant, as seen in the following architecture diagram:
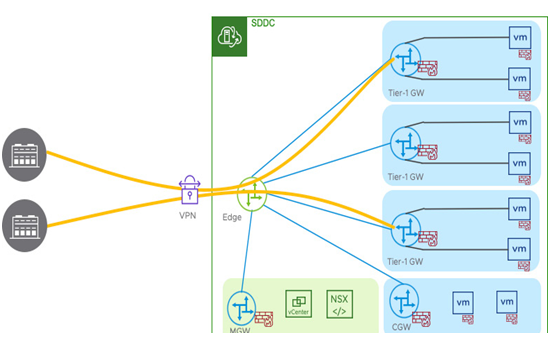
Figure 6.41 – Tier-1 gateway VPN termination diagram
The configuration is available at Networking | VPN | Tier-1 VPN Services, as seen in the following screenshot:
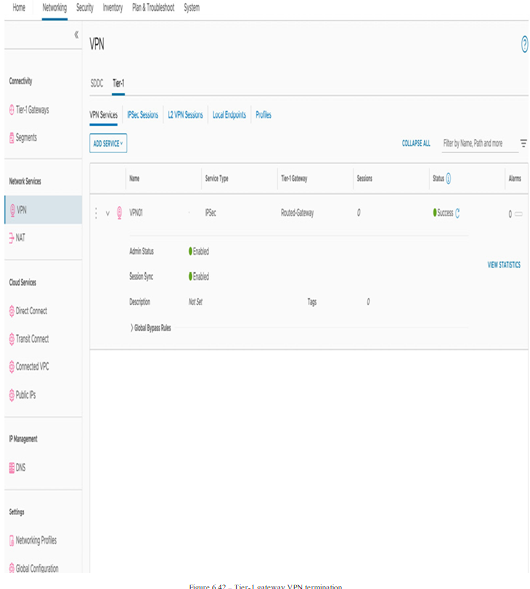
Figure 6.42 – Tier-1 gateway VPN termination
Information
Route-based VPNs terminating on Tier-1 Gateways do not support BGP; they support static routes instead.
Further configuration details can be found in the user guide at https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Cloud-on-AWS/services/com.vmware.vmc-aws-networking-security/GUID-5AF45CE6-FA53-45C0-83E5-25F8E3A055E9.html.
Connected VPC
Each VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC must be linked to an organization’s customer-managed AWS account. Inside the AWS account, organizations must create a VPC with subnets and connect it to the SDDC. This is referred to as the connected VPC.
The connected VPC setup is done during the SDDC provisioning process. You can review the configuration using the Connected VPC section in the Networking tab – the connection details of the AWS account will appear, including AWS Account ID, VPC ID, and VPC Subnet.
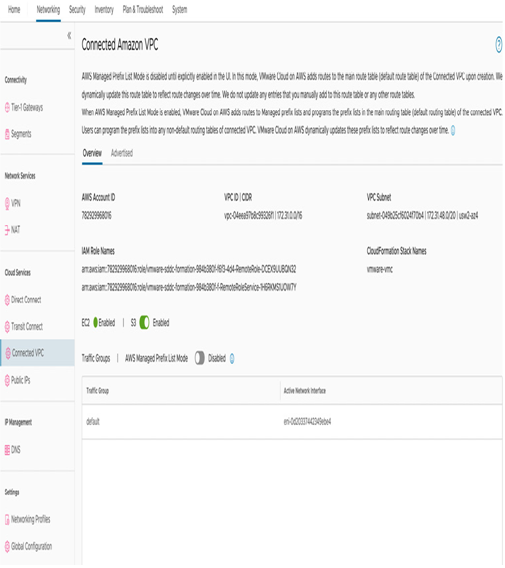
Figure 6.43 – Reviewing connected Amazon VPC information
Aggregation Prefixes Lists enables Route aggregation are used to create aggregate prefixes behind customer-configured Tier-1 gateways. The routes part of the Aggregated Prefix Lists will be advertised either on the INTRANET endpoint or the SERVICES endpoint. As shown in Figure 6.44, an Aggregation Prefix List named Connected – VPC with aggregated prefixes that include the 10.12.0.0/22 and 10.12.4.0/22 CIDRs is created and advertised over the SERVICES endpoint.
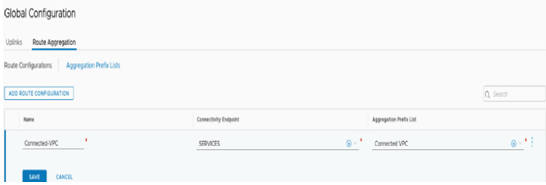
Figure 6.44 – Connected VPC route aggregation configuration
The Advertised tab in Connected Amazon VPC shows the same aggregated routes have been advertised. This can be seen in Figure 6.45:
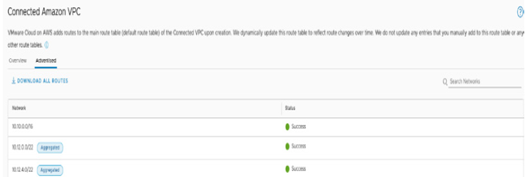
Figure 6.45 – Aggregated routes created using prefix lists advertised to connected VPC
Now that we have reviewed the connected VPC connectivity options, let’s review how to configure a Direct Connect connection in the SDDC.
Direct Connect
The VMware NSX version available with VMware Cloud on AWS has a number of features that were specifically developed for the service and are not available on any other NSX deployment. One of the most important is the ability to attach a DX Virtual Interface (VIF) directly from the NSX web interface.
While a thoughtful discussion about different DX design and deployment configurations is outside of the scope of this book, we still would like to mention a few important things to consider when using DX connectivity with a VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC:
- Both public and private VIFs are supported. However, only a private VIF can be used for hybrid cloud connectivity
- Attachment to a DX gateway through Transit Connect is supported
- You can use AWS-provided DX connectivity or opt for a cloud connectivity provider
- DX information is located on the Networking tab in the Direct Connect menu item:
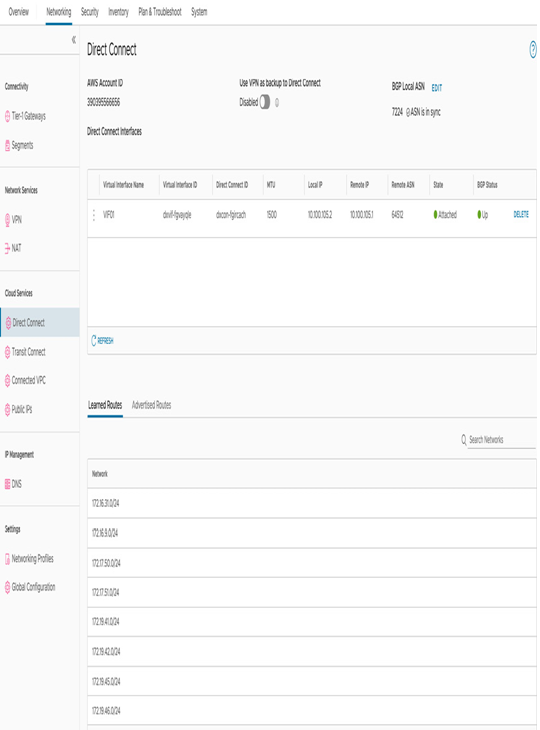
Figure 6.46 – Direct Connect configuration
The creation of a VIF should be performed in the AWS Management Console. You must export a VIF to the AWS account associated with the SDDC. You can find this account in the AWS Account ID field in the Direct Connect menu item.
Information
You can find further technical information on the VMware Cloud Tech Zone at https://vmc.techzone.vmware.com/resource/designlet-vmware-cloud-aws-sddc-connectivity-direct-connect-private-vif.

